
In this study, the authors tested whether the compound bromelain extracted from pineapples could protect skin cells from UV damage.
Read More...Protective effect of bromelain and pineapple extracts on UV-induced damage in human skin cells

In this study, the authors tested whether the compound bromelain extracted from pineapples could protect skin cells from UV damage.
Read More...Developing novel plant waste-based hydrogels for skin regeneration and infection detection in diabetic wounds

The purpose of this investigation is to develop a hydrogel to aid skin regeneration by creating an extracellular matrix for fibroblast growth with antibacterial and infection-detection properties. Authors developed two natural hydrogels based on pectin and potato peels and characterized the gels for fibroblast compatibility through rheology, scanning electron microscopy, swelling, degradation, and cell cytotoxicity assays. Overall, this experiment fabricated various hydrogels capable of acting as skin substitutes and counteracting infections to facilitate wound healing. Following further testing and validation, these hydrogels could help alleviate the 13-billion-dollar financial burden of foot ulcer treatment.
Read More...Developing a wearable, skin-based triboelectric nanogenerator
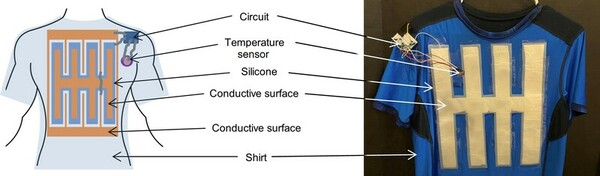
The authors designed a system that runs off of body heat to track body temperature that could help prevent injuries that result from elevated body temperature.
Read More...Characterization of Inflammatory Cytokine Gene Expression in a Family with a History of Psoriasis
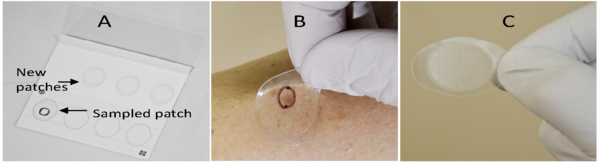
Psoriasis is a heritable autoimmune disorder characterized by abnormal red and itchy skin patches. The authors study the family of a man with psoriasis. They explore whether the man's children, who do not show any symptoms of psoriasis, demonstrate gene expression consistent with the disease.
Read More...Preliminary investigation of Allosauroidea facial integument and the evolution of theropod facial armor
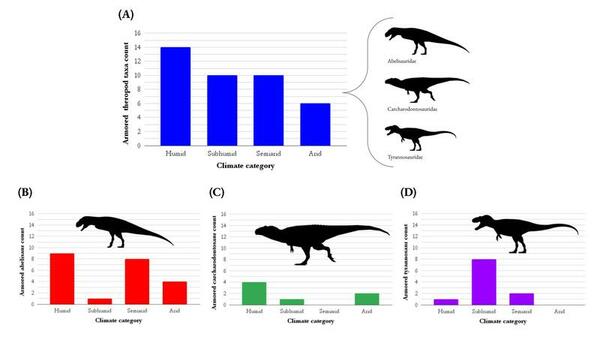
The facial integument, or external skin tissues, were assessed on set of dinosaurs from the Allosauroidea clade to test whether dermal patterns served specific functions.
Read More...Cutibacterium acnes sequence space topology implicates recA and guaA as potential virulence factors
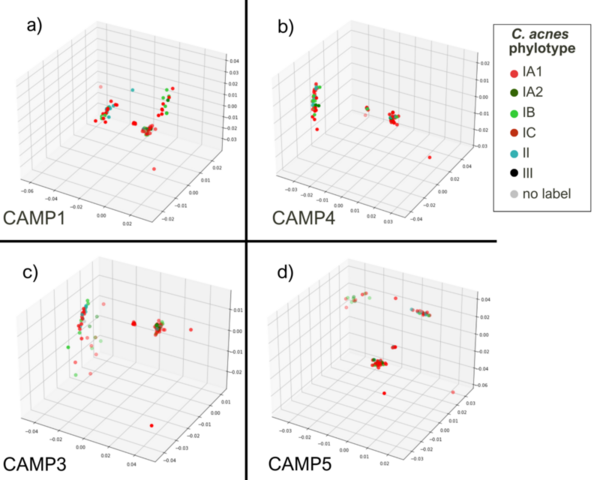
Cutibacterium acnes is a bacterium believed to play an important role in the pathogenesis of common skin diseases such as acne vulgaris. Currently, acne is known to be associated with strains from the type IA1 and IC clades of C. acnes, while those from the type IA2, IB, II, and III phylogroups are associated with skin health. This is the first study to explore the sequence space of individual gene products of different C. acnes phylogroups. Our analysis compared the sequence space topology of virulence factors to proteins with unknown functions and housekeeping proteins. We hypothesized that sequence space features of virulence factors are different from housekeeping protein features, which potentially provides an avenue to deduce unknown proteins’ functions. This proposition should be confirmed based on further experimental outcomes. A notable similarity in the sequence spaces’ topological features of previously known as housekeeping proteins encoded by recA and guaA genes to ‘putative virulence’ genes camp2 and tly was observed. Our research suggests further investigation of recA and guaA’s potential virulence properties to better understand acne pathogenesis and develop more targeted acne treatments.
Read More...Growth of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Escherichia coli when exposed to anti-acne vitamin A
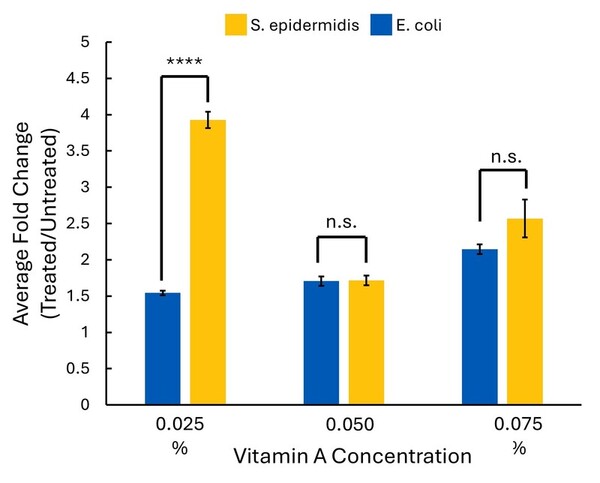
The authors looked at the impact of vitamin A (retinol) on growth of S. epidermidis (most abundant bacterium on the skin) and E. coli (found in the gut microbiome, but not on the skin).
Read More...Entropy-based subset selection principal component analysis for diabetes risk factor identification
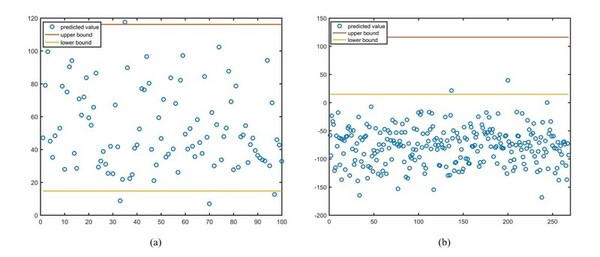
In this article, the authors looked at developing a strategy that would allow for earlier diagnosis of Diabetes as that improves long-term outcomes. They were able to find that BMI, tricep skin fold thickness, and blood pressure are the risk factors with the highest accuracy in predicting diabetes risk.
Read More...Durability of the Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) Patch Adhesive
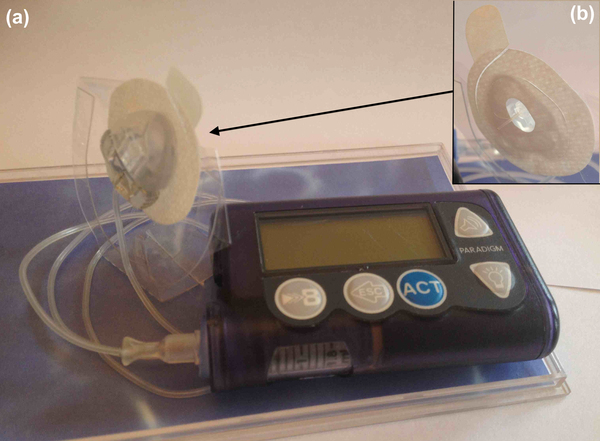
Insulin infusion patches are a common way for diabetics to receive medication. The durability of two different patch adhesives was compared on artificial skin with and without artificial sweat.
Read More...Unveiling the wound healing potential of umbilical cord derived conditioned medium: an in vitro study
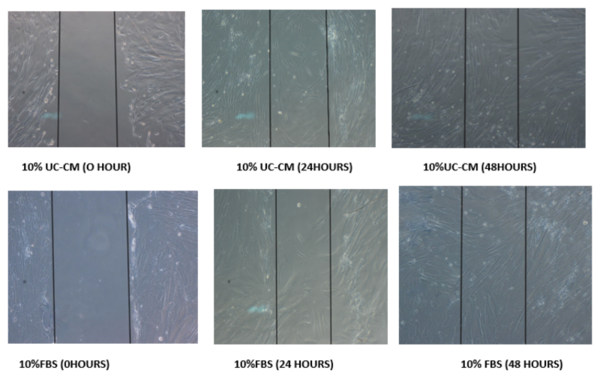
Chronic wounds pose a serious threat to an individual’s health and quality of life. However, due to the severity and morbidity of such wounds, many pre-existing treatments are inefficient or costly. While the use of skin grafts and other such biological constructs in chronic wound healing has already been characterized, the use of umbilical cord tissue has only recently garnered interest, despite the cytokine-rich composition of Wharton’s jelly (cord component). Our current study aimed to characterize the use of an umbilical cord derived conditioned medium (UC-CM) to treat chronic wounds.
Read More...