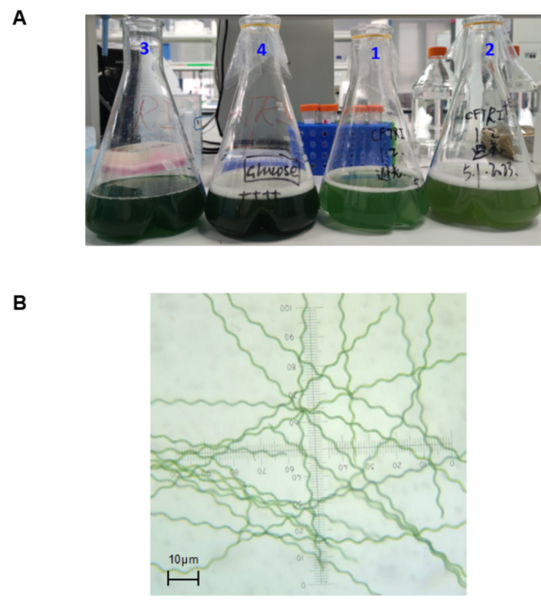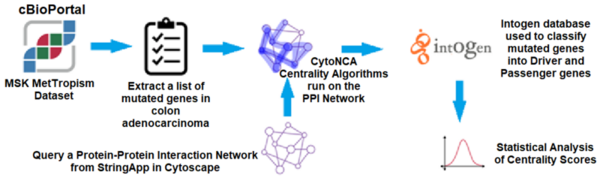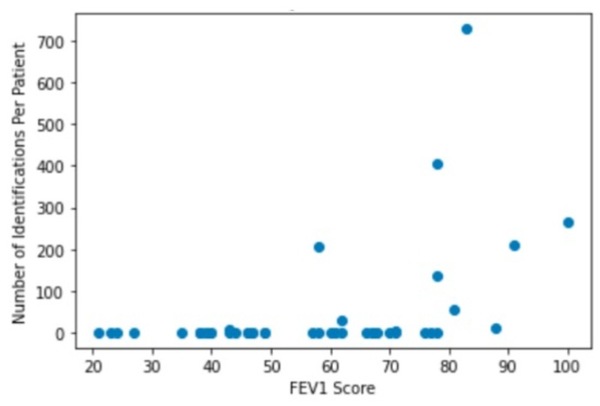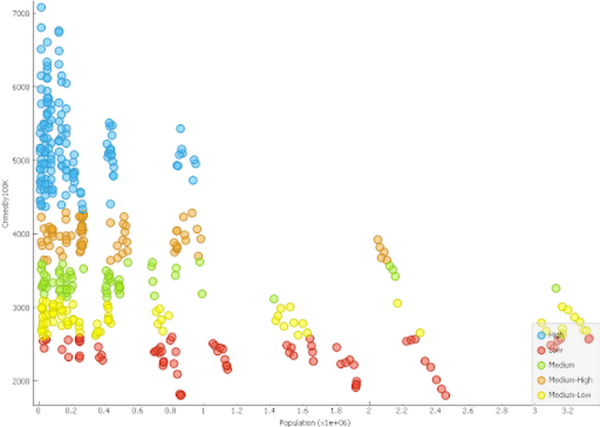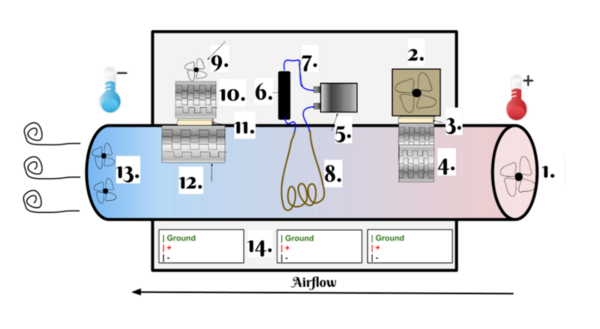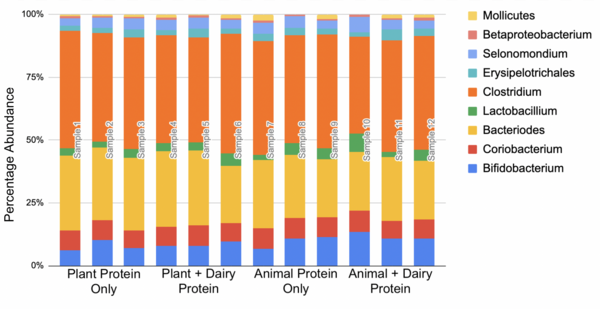
We know relatively little about how vegan diets and non-vegan diets compare when it comes to the gut microbiome. Gollamudi and Gollamudi tackle this challenge by investigating how changes in a participant's diet affected the diversity of their intestinal microbiome.
Read More...