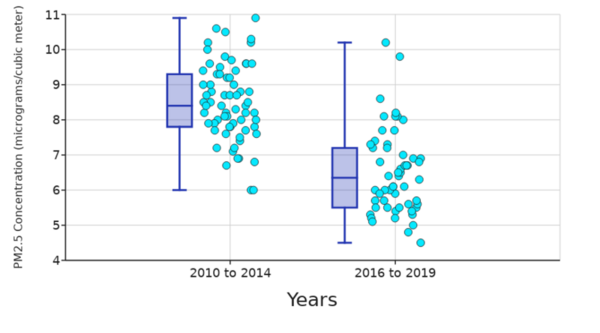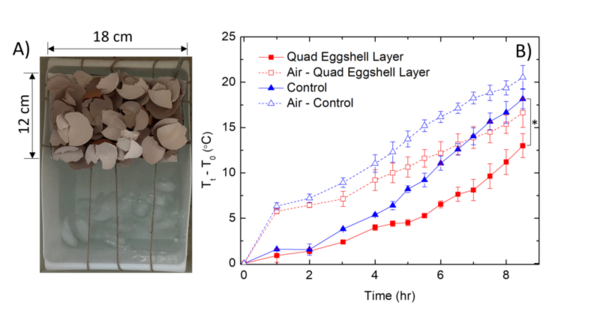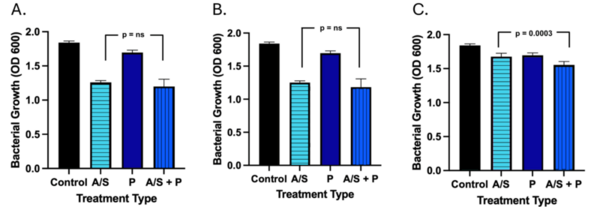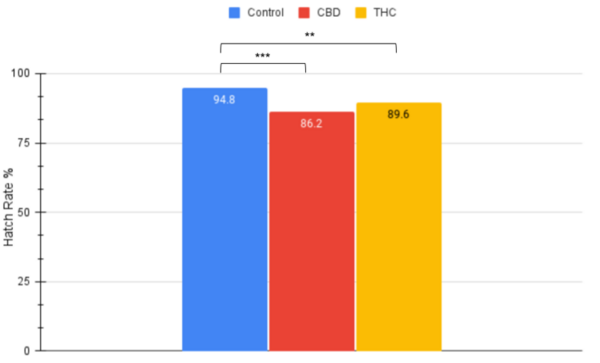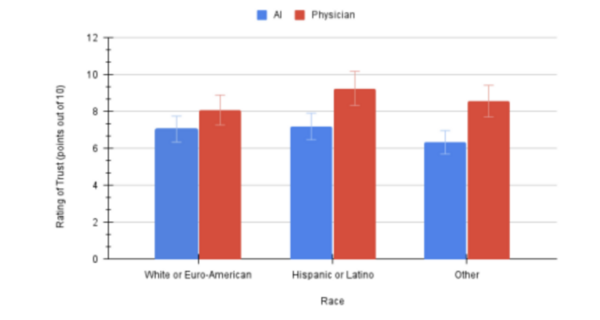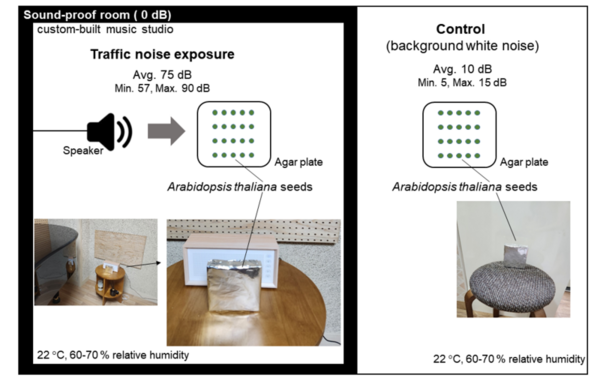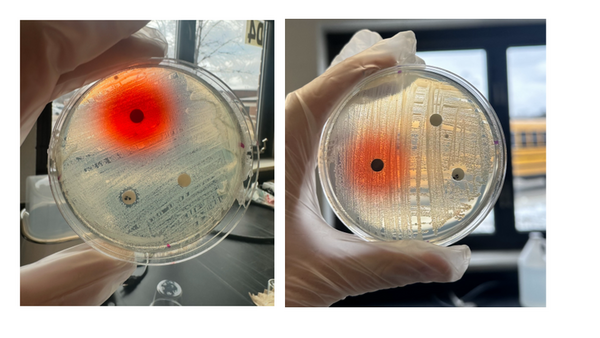
Here the authors aimed to compare the effects of artificial Allura Red AC dye and natural cochineal dye on the growth of Escherichia coli and Bacillus coagulans bacteria. Their research found that only Allura Red AC dye significantly affected bacterial growth, specifically amplifying E. coli growth. Based on their results, they suggest that Allura Red AC dye may increase the growth of E. coli bacteria within the human gut.
Read More...