Blockchain databases: Encrypted for efficient and secure NoSQL key-store
(1) Troy High School
https://doi.org/10.59720/22-084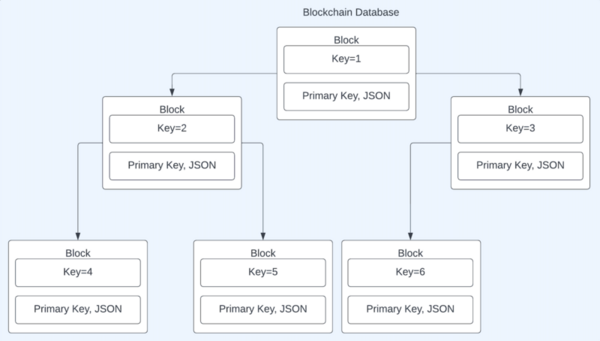
Databases have revealed many vulnerabilities in which hackers can penetrate and gain access to the data. Blockchains have been proven useful to protect against fraud and data miners, exemplified in cryptocurrencies. In this paper, we propose a blockchain database framework as a non-relational database structure that integrates the properties of blockchains and databases. The independent variables when testing this database were the Append, Delete, Query, and Update functions in the database framework. We predicted that the Append, Query, and Update functions would have a logarithmic runtime and linear throughput; while the Delete function would have a constant runtime and throughput. The database was tested with about 150,000 operations with the server and client locally running. We observed the runtime was slightly positively correlated while the Delete was not positively correlated with the number of operations in the Append, Query, and Update functions. The throughput of the Append, Query, and Update functions were significantly negatively correlated with the number of operations. The blockchain database framework displayed end-to-end encryption and feasibility with this experiment. One possible application of the database framework is in the financial industry, as there is a one-to-one correspondence with user and transaction.
This article has been tagged with: