Risk factors contributing to Pennsylvania childhood asthma
(1) North Allegheny Senior High School, (2) North Allegheny Intermediate High School
https://doi.org/10.59720/24-038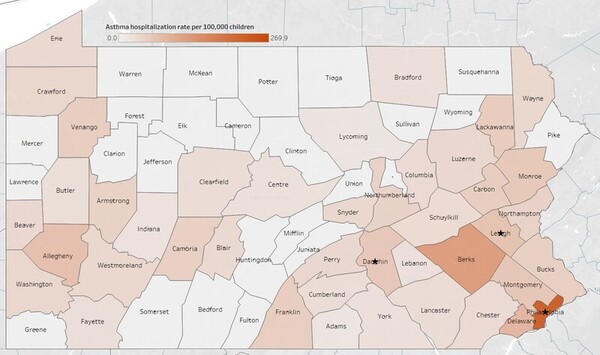
Childhood asthma continues to present a significant clinical and economic challenge in the U.S. Implementing more proactive treatment and comprehensive asthma management programs is imperative to addressing this national financial and health burden. Understanding the importance of various risk factors in asthma hospitalization and diagnosis rates can aid in earlier identification, treatment, and prevention of asthma altogether. In this study, we hypothesized that population density was the greatest predictor of childhood asthma hospitalization rate and diagnosis rate. We examined a total of 18 demographic, socioeconomic, and environmental risk factors at Pennsylvania’s county level to identify the risk factors contributing to childhood asthma hospitalization and diagnosis rate. Using a multiple linear regression model, we found “population density” and “percentage of Hispanic population” to be most strongly correlated with both childhood asthma hospitalization rate and diagnosis rates. In addition, “tobacco retail density”, “number of high ozone days”, and “childhood lead poisoning rate” were important factors associated with asthma hospitalization rate, while “percentage of population living in a rural area” was associated with asthma diagnosis rate. Our study provides a greater understanding of the influence of certain demographic and environmental exposures on Pennsylvania’s childhood asthma and emphasizes the importance of prevention.
This article has been tagged with: