A comparative study on the long-term effects of music and sports activities on cognitive skills of children
(1) James Logan High School, (2) Brain and Creativity Institute, University of Southern California
https://doi.org/10.59720/23-288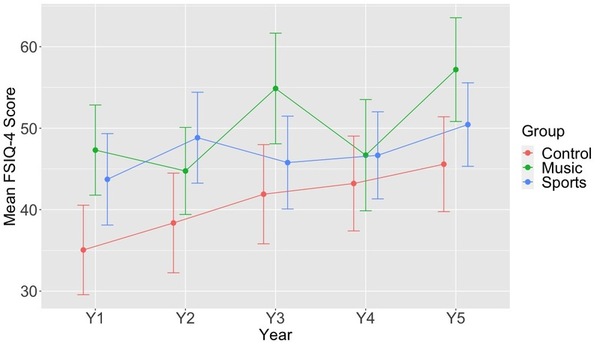
Learning music and engaging in sports have both been shown to develop cognitive skills in young children. With the rising incidence of learning disorders, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and dyslexia, in young children, understanding the impact of music and sports on cognitive skills in the developing brain is imperative. Our study aims to shed light on this topic by comparing three groups of children – those who learn music, those who practice sports, and those who don’t participate in either activity. We hypothesized a positive correlation between music and nonverbal cognitive skills and similarly between sports and verbal cognitive skills. Our dataset comprises the scores of Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence (WASI) to measure overall cognitive, nonverbal, and verbal elements of working memory. Analysis of this dataset reveals that students who participated in music performed better in tests assessing nonverbal intelligence, while children engaged in sports activities performed better in tests assessing verbal intelligence. Our results suggest that children who participate in music may show increased activity of the parietal cortex, which is responsible for nonverbal tasks, while children who participate in sports may show increased activity of the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for verbal tasks. Collectively, our results recommend music learning to improve math and mental manipulations for children with nonverbal disorders. Also, our results recommend sports participation to improve reading comprehension for children with verbal disorders. Future research with increased sample size is proposed for a better estimation of the WASI tests scores.
This article has been tagged with: