Effects of Prolonged Azithromycin Therapy on Bacterial Resistance to Functionally Analogous Antibiotics
(1) Olentangy High School, Lewis Center, Ohio
https://doi.org/10.59720/20-168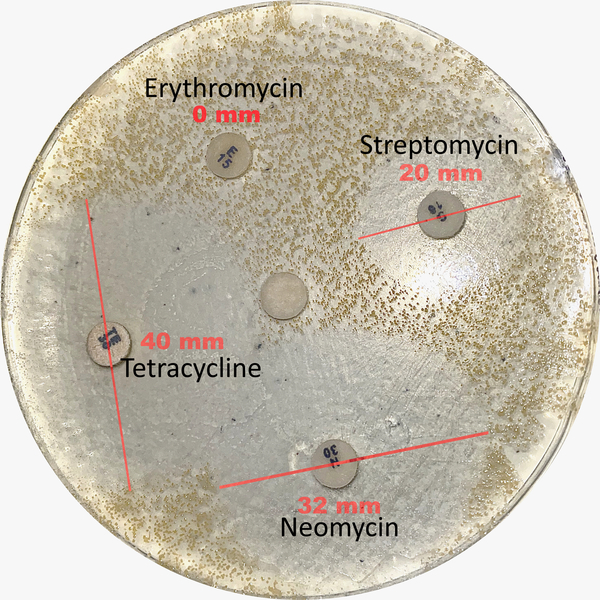
Bacteria may be innately resistant to antibiotics or acquire antimicrobial resistance through a variety of mediums. Under certain conditions, bacteria develop cross-resistance, a reduction in susceptibility to many antibiotics they have never been exposed to before. Most frequently, chemical similarities between antibiotics cause cross-resistance since bacterial defenses are counteractive to a specific molecule. However, cross-resistance to many chemically different antibiotics can occur when bacteria mutate to develop non-specific defenses. This study investigated a subject who had received prolonged azithromycin therapy for a neuropsychiatric condition related to chronic Group A Streptococcus infection. Given the possibility of cross-resistance, we hypothesized that, after prolonged azithromycin therapy, any bacteria collected from the subject would be resistant to structurally analogous antibiotics. We also hypothesized that, if bacteria from the subject had developed metabolic mutations, resistance to functionally analogous antibiotics would be present. From a series of antibiotic susceptibility tests, we concluded that the subject bacteria were resistant to erythromycin, a structural analog of azithromycin, but exhibited standard sensitivity to functional antibiotic analogs. The results of our study will help identify the risks associated with prolonged antibiotic therapy for a variety of conditions.
This article has been tagged with: